Myths and Facts About EEG Testing: What You Need to Know
Understanding EEG Testing
Electroencephalogram (EEG) testing is a crucial tool in diagnosing and understanding various neurological conditions. Despite its importance, there are many myths and misconceptions surrounding EEG tests. It's essential to separate fact from fiction to ensure patients have accurate information about what to expect from these tests.
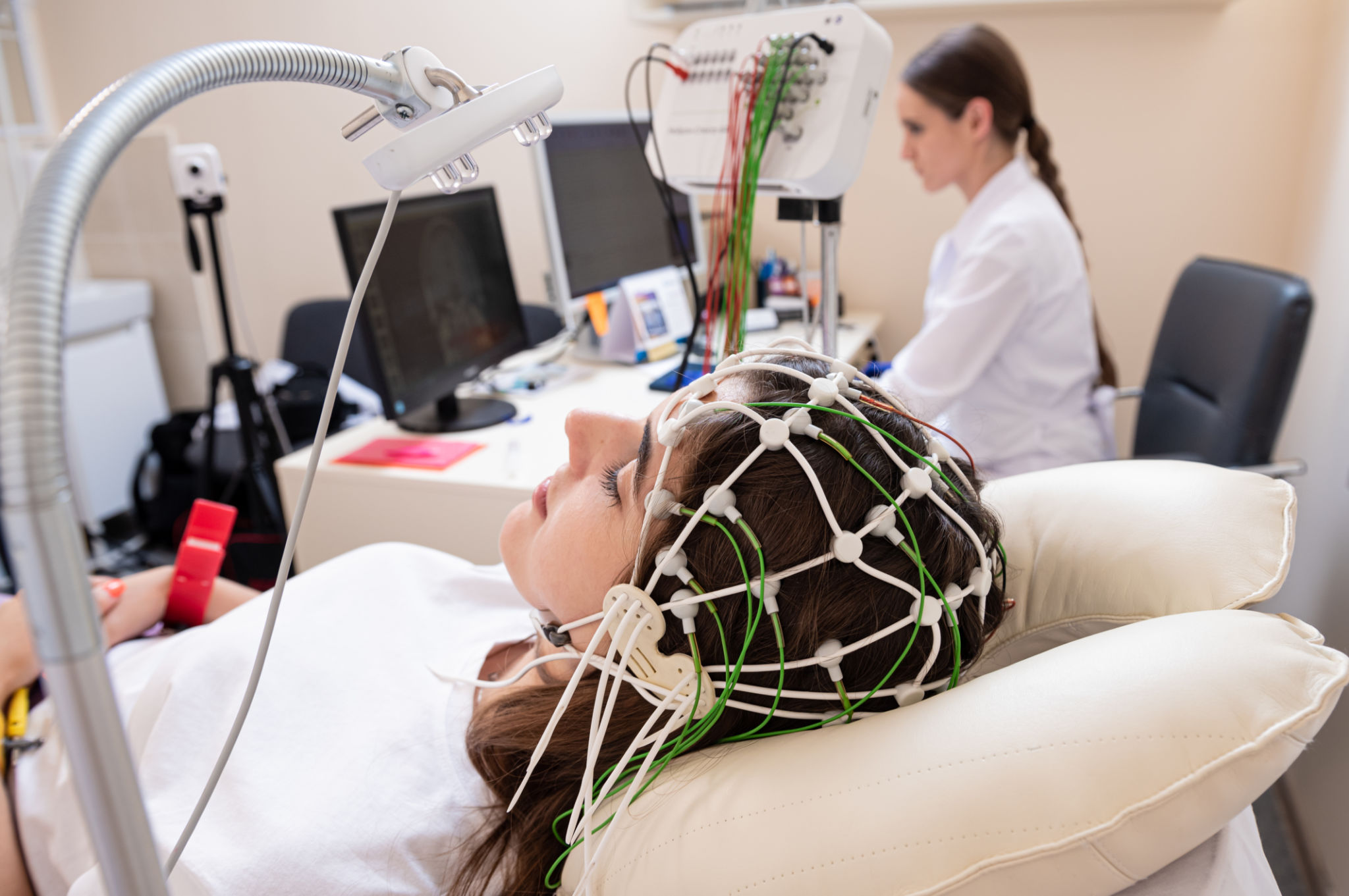
Myth: EEG Tests Are Painful
A common misconception is that EEG tests are painful. In reality, an EEG is a non-invasive procedure that should not cause any discomfort. During the test, small electrodes are placed on the scalp to measure electrical activity in the brain. These electrodes do not penetrate the skin, making the process completely painless.
Fact: EEGs Are Crucial for Diagnosing Seizure Disorders
EEGs play a vital role in diagnosing seizure disorders, including epilepsy. The test records brain wave patterns, which can help identify abnormal activity associated with seizures. This information is invaluable for neurologists to determine the best treatment plan for their patients.

How EEGs Work
Understanding the mechanics of EEGs can help demystify the process. An EEG measures the electrical signals produced by neurons in the brain. These signals are recorded and displayed as wavy lines on a computer or paper, allowing doctors to analyze brain activity.
Myth: EEGs Can Read Your Thoughts
Another myth is that EEGs can read your thoughts. While EEGs can monitor brain activity, they cannot interpret personal thoughts or emotions. The information gathered is limited to identifying patterns of electrical activity in the brain, which helps diagnose certain conditions.
Fact: EEGs Are Safe for All Ages
EEG testing is safe for both adults and children. There are no risks involved, making it suitable for patients of all ages. The procedure does not involve radiation or any harmful substances, ensuring it's a secure option for diagnosing neurological issues.
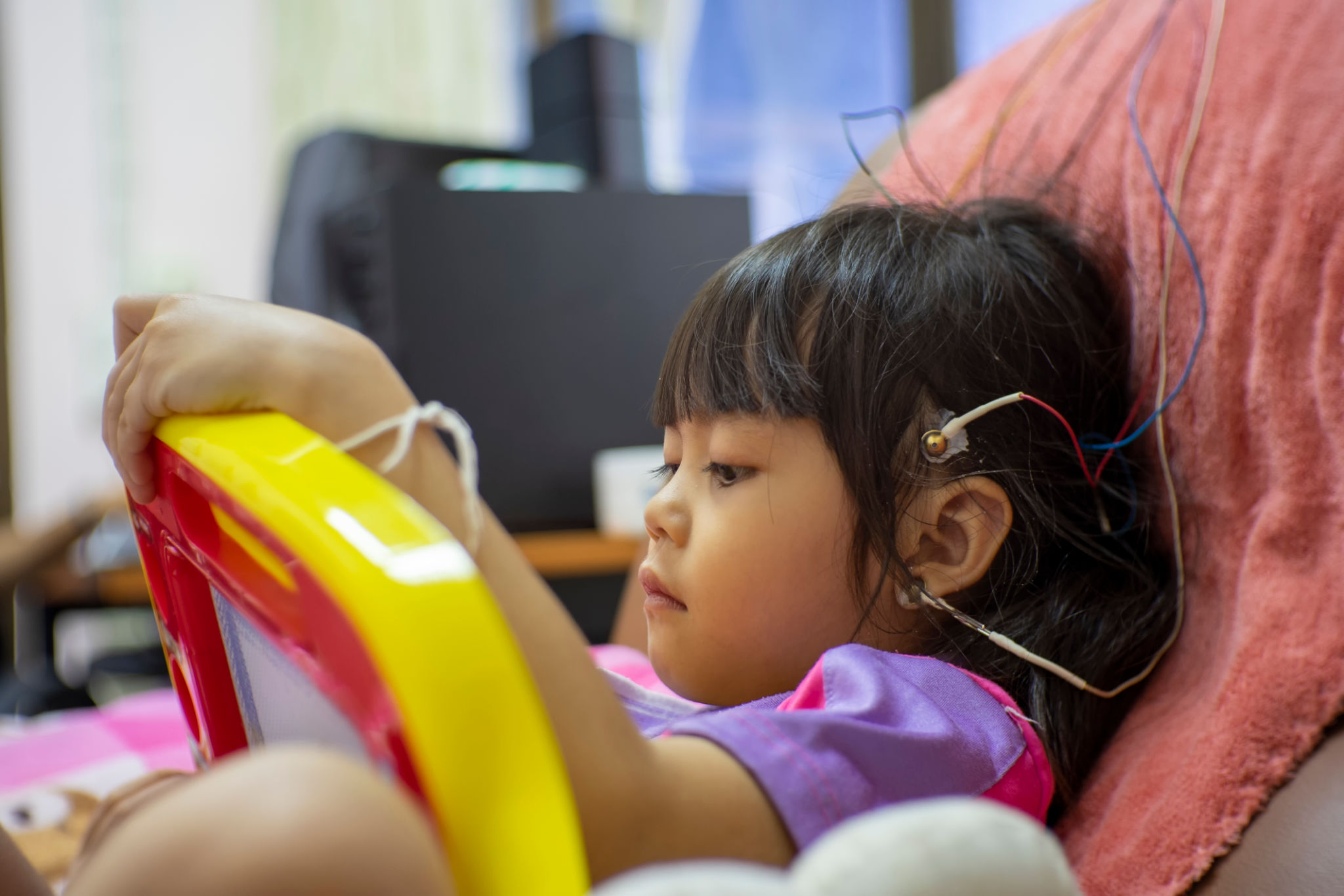

Preparing for an EEG Test
Before undergoing an EEG, patients should follow specific guidelines to ensure accurate results. Typically, individuals are advised to avoid caffeine and any medications that may affect brain activity unless directed otherwise by their healthcare provider.
Myth: EEGs Are Only for Diagnosing Epilepsy
While EEGs are commonly used to diagnose epilepsy, they are also helpful in assessing other conditions such as sleep disorders, head injuries, and brain infections. The versatility of EEG testing makes it a valuable diagnostic tool in many neurological assessments.
Fact: EEG Results Require Expert Analysis
The data collected from an EEG test can be complex and requires interpretation by a trained neurologist. They will analyze the patterns to provide a comprehensive diagnosis. Patients should discuss their results with their healthcare provider to understand what the findings mean for their specific situation.

By dispelling these myths and understanding the facts about EEG testing, patients can approach the procedure with confidence and clarity. Knowing what to expect can alleviate concerns and ensure a smooth experience, paving the way for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.